Axiom App Architecture
Axiom provides smart contracts trustless access to all on-chain data and arbitrary expressive compute over it. To integrate Axiom into your on-chain application, follow the following steps:
- Specify a query into Axiom by writing a special client circuit using our Typescript SDK.
- Implement a callback on your dapp smart contract to receive ZK-verified results from the
AxiomV2Querycontract upon query fulfillment. - Run your client circuit to create and send queries from command line, script, or web browser to the
AxiomV2Querycontract on-chain so Axiom can fulfill your query and call your dapp's callback function.
Axiom is not an indexer like The Graph, which provides data for human consumption. Instead, Axiom makes previously inaccessible on-chain data like transactions and receipts available to smart contracts in a trustless way with ZK.
Axiom Integration Flow
Here is a simplified diagram of how Axiom would fit into your on-chain application:
The results of your query are only trustlessly verified and safe to use after Axiom has fulfilled your query and the AxiomV2Query contract calls your callback function.
For a more detailed explanation of what happens inside the Axiom box, read on:
Writing a Client Circuit with Axiom Subqueries and ZK Primitives
Axiom makes it easy for smart contract developers to write circuits that enable access to historical on-chain data and perform compute on that data. To make writing those circuits easy, we provide two types of functions in our SDK that leverage the circuit libraries that we've already built: Axiom Subqueries and ZK Primitives.
Axiom Subqueries
Axiom Subqueries allow developers access to any historical on-chain data for their smart contracts. Axiom will prove these subqueries in ZK, which enables trustless access to on-chain data including anything in the Ethereum storage, state, transactions, and receipt roots. Here are some examples of some of the functions that we provide, which you can leverage when building your client circuit:
Header Subquery
const header = getHeader(blockNumber);
Account Subquery
const account = getAccount(blockNumber, address);
Storage Subquery
const storage: Storage = getStorage(blockNumber, address);
Solidity Nested Mapping Subquery
const mapping: Mapping = getSolidityMapping(blockNumber, address, slot);
Transactions Subquery
const tx: Tx = getTx(blockNumber, txIdx);
Receipts Subquery
const receipt: Receipt = getReceipt(blockNumber, txIdx);
For a complete list of all of the Axiom Subqueries available, see the Axiom Subqueries page in the SDK docs. To learn more about how to find commonly used types of on-chain data, see Finding Storage Slots and Receipts and Logs.
ZK Primitives
ZK Primitives allow developers to specify computations on the data retrieved by Axiom Subqueries. These compute circuits allow for computations on data to be performed off-chain in ZK that would otherwise be impractical on-chain. Here are some examples of the ZK Primitives that we provide:
- Arithmetic Operations:
add,sub,neg,mul,div,mod,pow - Boolean Logic and Selection:
or,and,not,select,selectFromIdx - Comparison:
isZero,isEqual,isLessThan,checkEqual,checkLessThan
For a more complete list and more detailed description of all of the ZK Primitives available, see the ZK Primitives page in the SDK docs.
Proof Aggregation and Verification
One distinction between Axiom Subqueries and ZK Primitives is that the proofs for Axiom Subqueries are fulfilled by Axiom, while the proofs for ZK Primitives are generated on the client side. Axiom will aggregate all proofs into a single proof that validates all of the computations specified by the developer, which will be verified on-chain. Once verified on-chain, your smart contract can use the results while incurring no additional trust assumptions on top of Ethereum itself.
How to Use Axiom
We've provided a general flow for a common way your app, third-party services, and Axiom can fit together. The user flow for Axiom involves the following steps:
- Construct an Axiom query on your app frontend or backend using the Axiom SDK. This will involve fetching inputs from a JSON-RPC node or indexer and running a client ZK circuit on those inputs using the SDK. Once constructed, you send the query on-chain to the
AxiomV2Querycontract. - Axiom will index the query, compute the result, and generate a ZK proof of validity. The result and proof are sent on-chain and verified in the
AxiomV2Querycontract. - Finally, Axiom will atomically call the user-specified callback on your smart contract with the ZK-verified results of your query. Your smart contract can then use these results trustlessly for your application.
A visual illustration of this flow is in the diagram below:
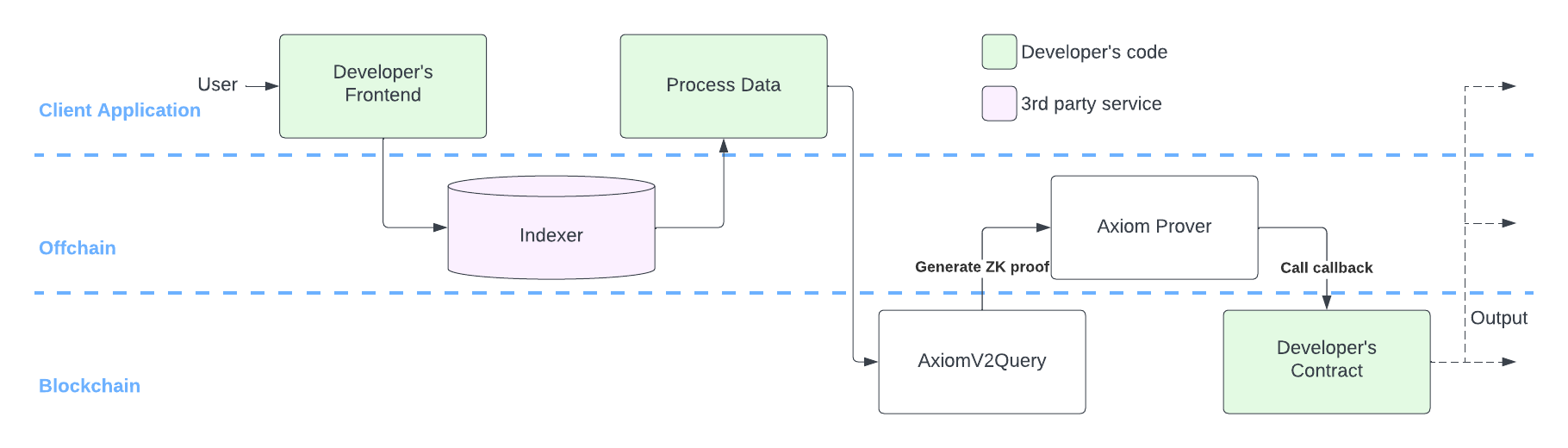
See Gas, Pricing, and Limits for details on how Axiom charges per query and the limits of a single query.
The remaining pages in this section explain how to:
- Write an Axiom client circuit
- Integrate it into your smart contract
- Test your Axiom integration using our Foundry test extension
- Deploy your Axiom app in production
